Health Research Needs Assessment
Health Translation Queensland (HTQ), in collaboration with its partners, has undertaken a comprehensive health research needs assessment to assist with identifying and responding to health research translation needs, emerging health priorities and funding opportunities across Queensland.
HTQ’s Health Research Needs Assessment (needs assessment) identifies significant trends and issues in demographic and health data, as well as gaps and opportunities for collaboration at a statewide level – in a first providing unique insights into the health translation landscape across all of Queensland. The needs assessment also considered health research needs that can be addressed by both research translation and service provision - which sets it apart from other more locally focused needs assessments which primarily focus on health service provision.
HTQ and the report’s lead author Emma White used a methodical and thorough needs assessment approach drawing on vast sets of credible data sources and extensive stakeholder and consumer consultations to bring together demographic and health data that is meaningful in a Queensland-wide context.
The needs assessment is a substantial research piece that incorporates research evidence through data and literature, practical experience through key stakeholders, clinicians and researchers, as well as lived experience through consumers as forms of evidence in identifying health research priority areas.
Through the needs assessment HTQ has identified 9 health research priority areas, each with potential focus areas and collaborative opportunities.
The 9 health research priority areas are (in alphabetical order):
- ageing and aged care
- chronic conditions
- health system improvement
- health system preparedness
- maternal, child and adolescent health
- mental health
- palliative and end-of-life care and adolescent health
- primary health care, including community and preventative care
- rural and remote communities.
Going forward, the needs assessment will be used by HTQ to establish HTQ Collaborative Groups for identified health research priority areas. The purpose of HTQ’s Collaborative Groups is to advance research translation projects united around a specific clinical problem or priority population group to respond to emerging health priorities and harness funding opportunities.
Download the full Health Research Needs Assessment report.
Download the Health Research Needs Assessment summary (infographic).
Download the Health Research Needs Assessment survey findings (infographic).
Key points:
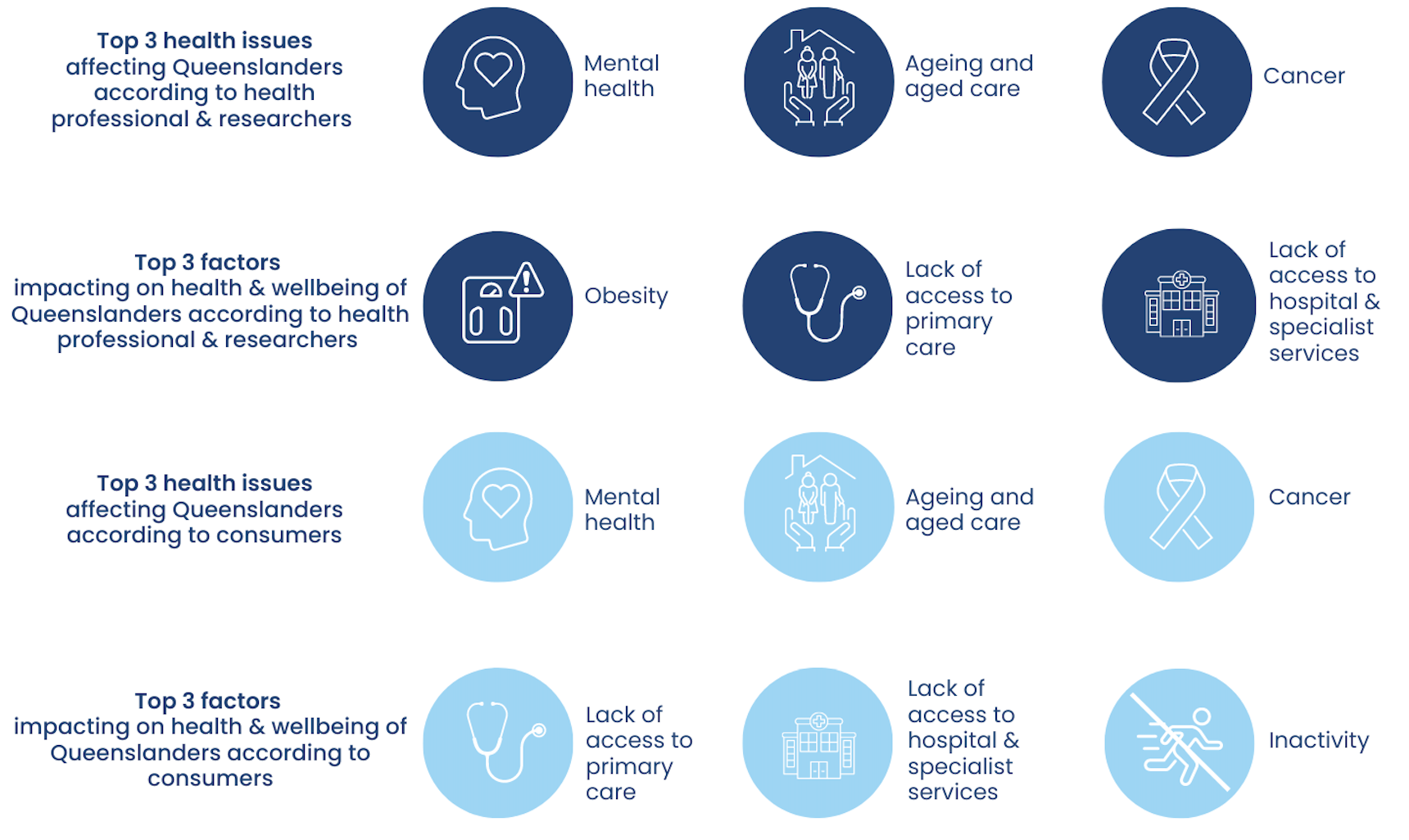
- Ageing and aged care
- Queensland’s population is ageing. This will have a substantial impact on the burden of disease and health service use.
- Aged care was identified by health professionals, researchers and consumers as a major health research need.
- Ageing and aged care is a Medical Research Future Fund (MRFF) priority area, presenting a potential funding opportunity.
- Potential focus areas within ageing and aged care:
- Chronic conditions
- Leading causes of death are dominated by chronic conditions.
- Chronic conditions contribute substantially to potentially preventable hospitalisations.
- Chronic conditions is a MRFF priority area, presenting a potential funding opportunity.
- Potential focus areas within chronic conditions:
- Diabetes
- Chronic lower respiratory disease
- Arthritis (rheumatoid and osteoarthritis)
- Chronic pain
- Health system improvement
- Health research is often focused on treatment and care, rather than on health care systems.
- Improving health systems and processes could have significant impact on care delivery and the subsequent health of communities and individuals.
- Potential focus areas within health system improvement:
- System integration
- Service coordination
- New models of care
- Workforce
- Health system preparedness
- The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for improved health system preparedness.
- Potential focus area within health system preparedness:
- Health system capacity and management
- Maternal, child and adolescent health
- Reproductive and maternal conditions experienced the highest increase in burden of disease between 2011 and 2018 (37.9%).
- Potential focus areas within maternal, child and adolescent health:
- Maternal health in the perinatal period
- Models of maternity care
- Child and adolescent mental health
- Mental health
- Mental health is a major cause of burden of disease in both children and adults. It is also a major cause of hospitalisations, a trend which is increasing.
- Mental health was identified by health professionals, researchers and consumers as a major need.
- Potential focus areas within mental health:
- Suicide and self-harm
- Alcohol and other drugs
- Children and adolescent mental health
- Rural and remote communities
- Palliative and end-of-life care and adolescent health
- The ageing population and increase in chronic disease means the way palliative and end-of-life care is currently delivered needs to evolve.
- Palliative and end-of-life care present a significant cost to the health care system.
- Potential focus areas within palliative and end-of-life care:
- Advances in technology and treatment options
- System change
- Improved data collection and data sharing
- Primary health care, including community and preventative care
- Quality primary health care is a key enabler for good health and effective health care systems.
- Improved access to primary health care (e.g. general practice and allied health) was identified by consumers, health professionals and researchers as a major need.
- The rate of potentially preventable hospitalisations increased by 23% from 2012-13 to 2017-18, suggesting greater support for primary health care is needed.
- Approximately 38% of the burden of disease could be prevented by reducing or avoiding exposure to modifiable risk factors.
- Health risk factors also contribute substantially to health care costs.
- Primary health care is a MRFF priority area, presenting a potential funding opportunity.
- Potential focus areas within primary health care, including community and preventative care:
- Overcoming research challenges in primary health care
- Obesity
- Nutrition
- Alcohol and other drugs
- Rural and remote communities
- Life expectancy, health-adjusted life years and burden of disease are all adversely impacted by rural and remoteness.
- This has a significant impact on health care costs and service delivery in rural and remote communities and major cities (due to many people having to travel to major cities to access services).
- Potential focus areas within rural and remote communities:
- Innovative service delivery models
- Aged care
- Mental health
- Other health needs impacting rural and remote communities
- Areas of lower socioeconomic status
- Queensland’s population snapshot (as of 2020)

- Queenslanders health snapshot (as of 2020)
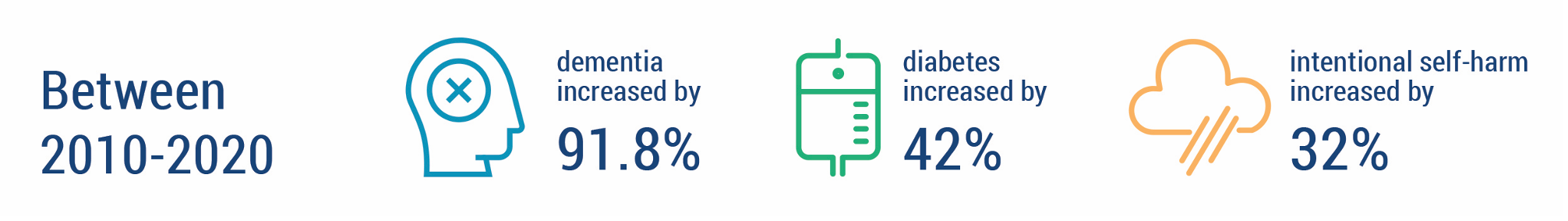
- Queenslanders leading cause of death by age

- Findings of consumer and health professional/researcher surveys